POINT OF SALE SYSTEM: KEY COMPONENTS & PERKS
Article by Nicholas. Updated December 22, 2020
A point of sale system, also known as POS, refers to the position where clients make payments for your products and/or services at your store. It acts as the central business component that merges customer, sales, & inventory management.
As of today, statistics show that 50% of single-store retailers have yet to implement one. Instead, many still prefer using the conventional bookkeeping method such as Excel, cash registers, or QuickBooks. While these methods are less costly and are more comfortable to be used due to familiarity, retailers become more vulnerable to face a slowdown in their operations. The reason being, retailers lack critical data that could accelerate their businesses. On the other hand, a POS system provides detailed information such as customers' key insights, inventory levels, and more.
But before we look into its perks, let us first grasp its key components!
1.0. COMPONENTS
Every POS system has software and hardware components, the essential duos that elevate your business' daily operations to a whole new level of efficiency.
1.1. SOFTWARE COMPONENTS
There are two types of software components (On-premise POS and Cloud POS).
On-premise POS systems are the traditional ones that operate within an internal network. Local servers are used for information storing purposes. Simply put, the functionality is similar to your personal computer where you use programs to save data on your local drive. The data is accessible only from the local server or by using an alternate web application.
Cloud-based POS software is the latest product in the POS market that leverages cloud technology, allowing users to access the platform whenever there is an Internet connection. It complements well with most POS hardware such as printers and cash registers. Moreover, the comfort level and benefit that this product offers are unmatched due to its mobile-friendliness.
1.2. HARDWARE COMPONENTS
Aside from software, below shows the physical components to get your POS to function:-
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
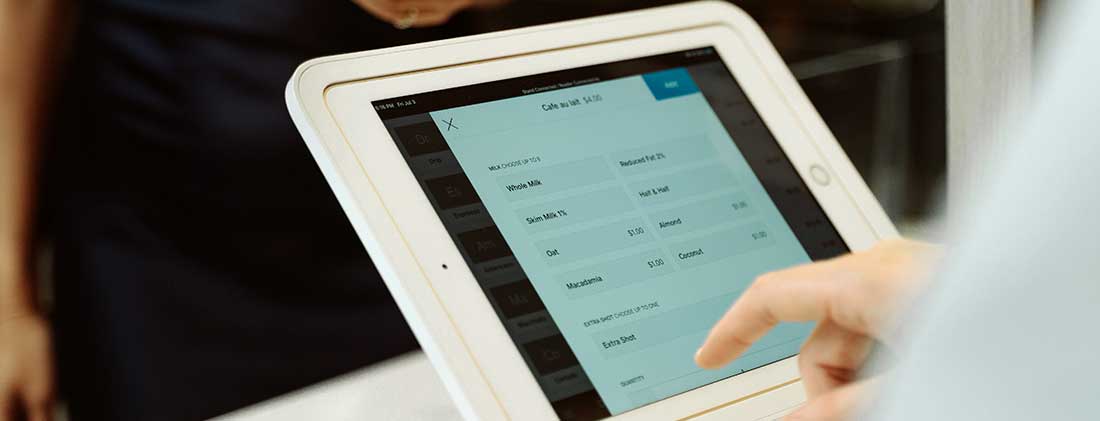
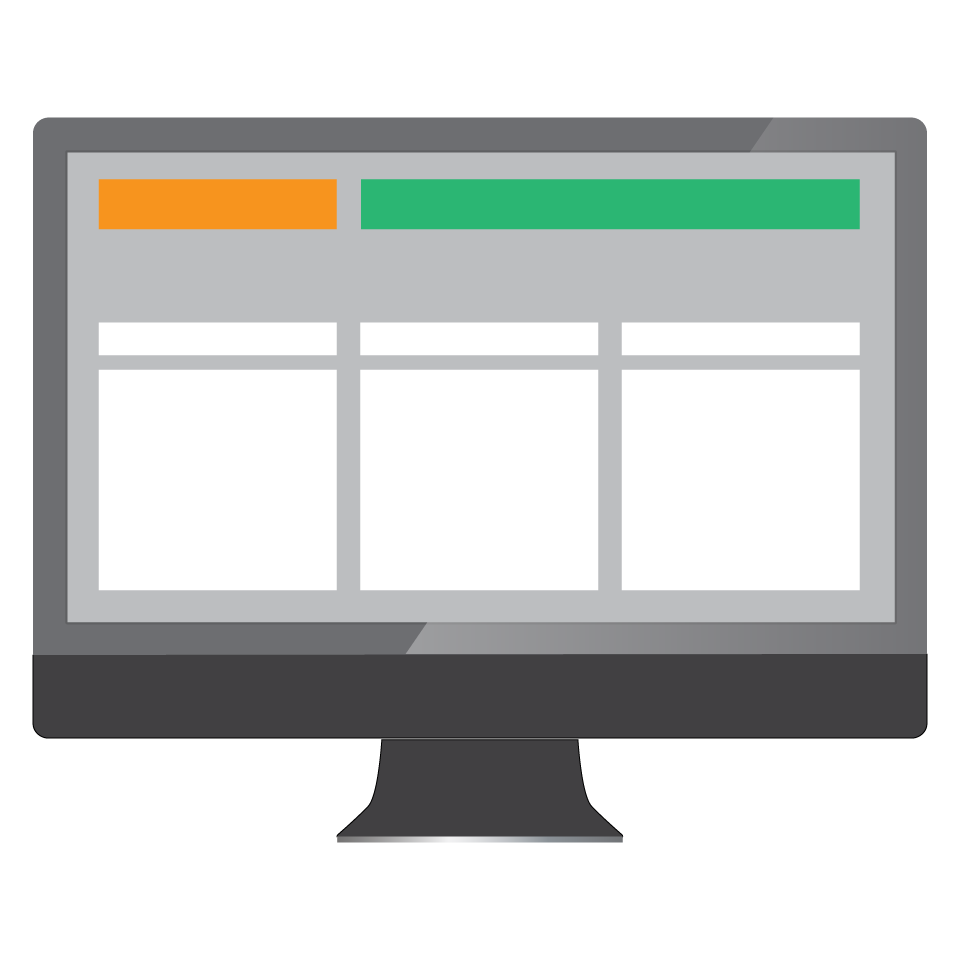 Monitor Monitor |
Presents the products database and displays sales reports. Currently, tablets, especially iPads, are slowly replacing monitors due to their user-friendliness and low cost. These features make them the ideal choice for small businesses with a tense budget. |
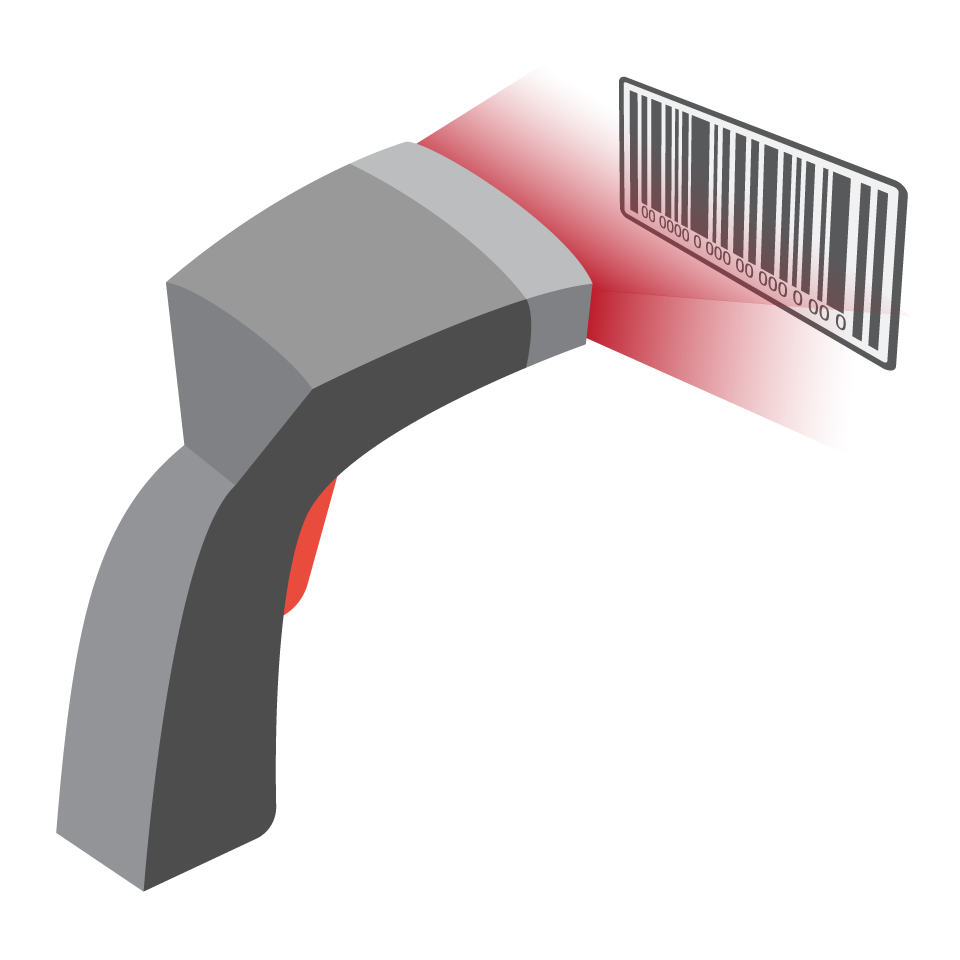 Barcode scanner Barcode scanner |
Scans barcodes on products to pull their information for checkout automation processes. It is also to ensure the inventory management system adjusts the stock levels automatically, accurately, and correctly. Barcode scanners can be handheld by employees to check out bulky products, or they can stationary where items are passed over the laser to check out the items. In normal scenarios, stationary barcode scanners are more efficient in large volumes of transactions. |
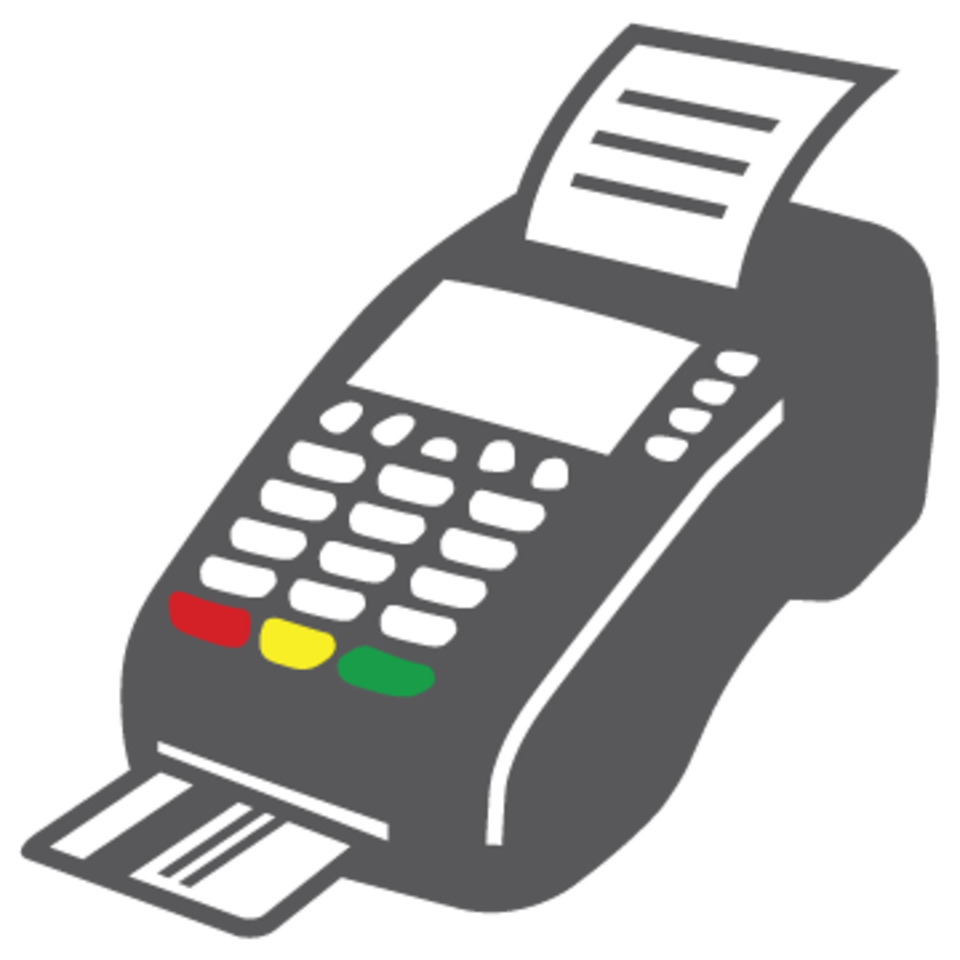 Card Terminal Card Terminal |
This is also another essential component of a POS hardware bundle. More and more consumers prefer to pay by plastic using credit or debit cards as holding too much cash can be quite a hassle nowadays. Moreover, the card reader should be able to accept contactless payments, EMV, and swiped transactions. |
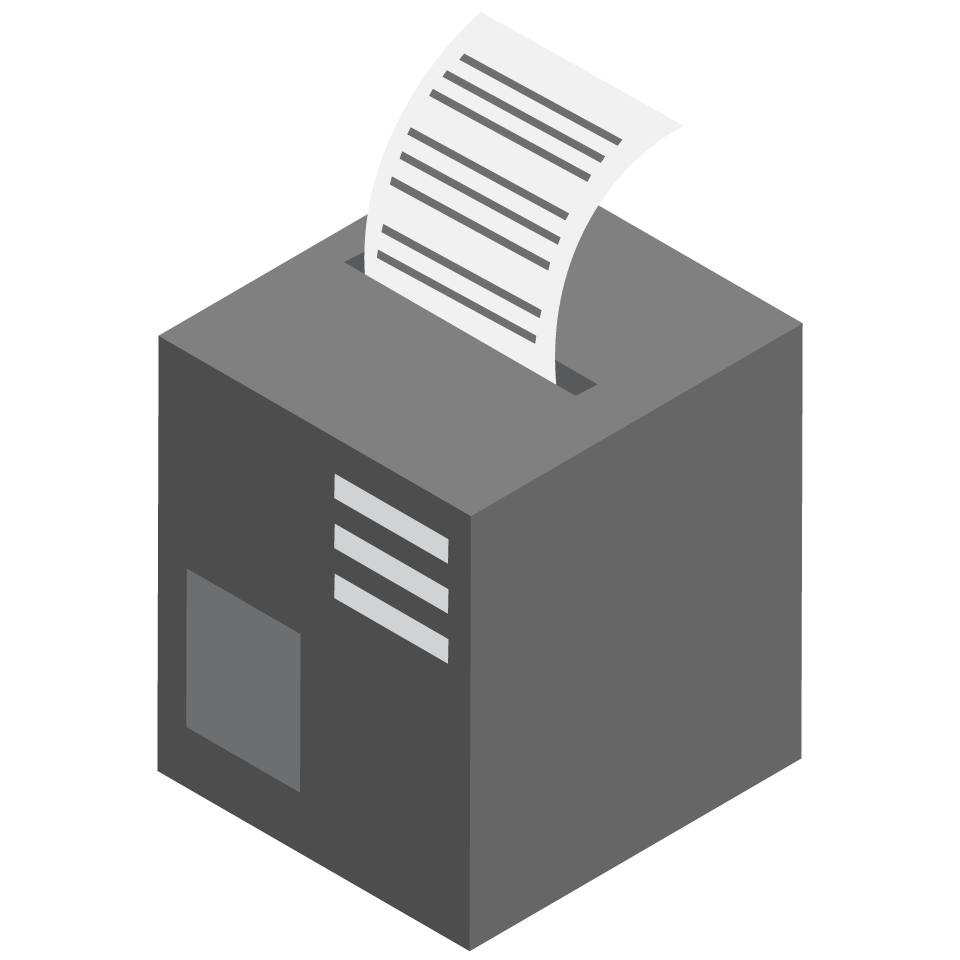 Receipt printer Receipt printer |
After every transaction, it is a common courtesy to give the customer a record of it. This record is called a receipt which is produced by a receipt printer. Customers need receipts as a medium to get a refund if the item bought is not of good quality or proof when filling in the claim form. Although text receipts and emails are gaining popularity, paper receipts are still as important in giving customers a physical snapshot of their record. |
 Cash drawer Cash drawer |
Of course, people still pay by cash hence; having a cash drawer is a must. It has been dominant since the early retail days and although more consumers are into cards as their preferred payment method, it is not disappearing any time soon. It keeps the cash proceeds for a specific period and acts as the medium for cash payment & balance change in return. |
2.0. PERKS
2.1. BUSINESS EFFICIENCY & SECURITY

A business’s efficiency is measured by how fast it converts inputs (labor, capital, materials) into outputs (revenue, products & services).
In the case of a POS system, its implementation is appealing and rewarding to both sellers and buyers. The functionalities of its software and hardware components that complement each other can facilitate quicker checkout time; hence more transactions can be done immediately with the lesser time needed. Moreover, paperwork, bill, and report managements become more time-saving thanks to different features in the POS system such as barcode scanner, card terminals, and more. The system also records every transaction made and acts as the safe-keeper of the data; hence customers do not need to worry about their particulars being leaked out.
2.2. INVENTORY MANAGEMENT & CONTROL

A business’s success is not always measured from a high sales amount. Inventory management also plays a vital role in it because it allows business owners to keep track of every product offered, whether in the storeroom or on display. It also eliminates inefficiencies such as manual inventory count which is time-consuming. By utilizing a POS system, inventory will adjust accordingly and automatically when goods are sold. Business owners are sure to know when an item’s supply runs low and requires re-ordering. They can also be notified if certain items are not making them sales; hence quick actions can be taken such as cutting down on their purchasing units from suppliers.
2.3. ACCOUNTING & FINANCIAL REPORTING

With accounting software in the POS system, every transaction can be tracked accurately and placed into proper accounting categories. Business owners will then use these data to generate monthly or quarterly reports needed for tax reasons and also financial reporting. Financial reporting is for the sole purpose of disclosing financial results and other relevant information to stakeholders such as customers, investors, and regulators on a company’s performance over a fixed time. The financial reports issued include:-
- Balance Sheet or Statement of Financial Position (SOFP) – Reports on a company’s assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity.
- Income Statement or Profit and Loss Statement (P&L report) – Reports on a company’s income, expenses, and profits. Sales and expenses incurred are also included. .
- Cash Flow Statement – Provides figures of a company’s cash inflows and cash outflows during a specified period. These cash sources and uses include operating, investing, and financing activities.
- Retained Earnings Statement – A more detailed equity statement that outlines a company’s retained earning changes over a specified period.
2.4. SALES REPORTING & ANALYTICS
Sales reporting & analytics allow users to capture, extract, and analyze their store’s sales data. Through reports and figures, a real-time snapshot of the store’s performance is given. This concrete data assists owners in making better decisions in improving sales and profitability. Sales reporting & analytics do just that by delivering visibility and transparency into users’ full operation. Besides keeping track of products that top the selling board automatically, how much revenue each product makes is disclosed too.
Let’s take a clothing retail shop as an example. Imagine your business is really good and you can sell many clothes in a short period, the thing you need to do, and probably the last thing you would want to do is to manually update your inventory which can be a hassle. Fortunately, with real-time sale reporting, you will automatically receive alerts when inventory levels drop below a specified threshold amount. A POS system has exactly that and you will never run out of best-selling items.
2.5. CUSTOMER MANAGEMENT & E-COMMERCE

There are many factors affecting the sales revenue – the company’s product, marketing strategy, cost efficiency, etc. While these elements are essential, studies show that most businesses tend to overlook an underrated element that is equally important which is customer management. Customers are more likely to visit your store frequently as their needs & preferences are matched & recognized. This is where POS comes into play. A POS system is able to track all customer data with its customer relationship management (CRM). Precisely, a POS system should be able to exercise the following:-
- Track customers’ purchase history.
- Record purchasers’ general information such as name, age, birthday, phone number, email address.
- Utilize email marketing to promote products or for follow up purposes.
Nowadays, most businesses have their digital stores set up. Customers find them convenient and often search them up to research on the products offered before stepping into their brick and mortar store to test them out. With their research, businesses recognize what customers are looking for and how they respond to their products. In fact, businesses could also find out the shopping trends that might have been lacking in-store. These insights too will allow businesses to make quick amendments to both their physical and digital stores such as promotions, discounts, etc. Moreover, customer data can also be inputted from their researches.
In summary, with proper customer management, stored data can be analyzed to develop strategies on how to improve its e-commerce via digital and physical store. On the other hand, more researches from digital store mean additional customer information; hence an even more accurate analysis can be deduced. In other words, customer management and e-commerce somewhat rely on each other to further escalate their respective potentials.